Modulation is the process of making some message signal suitable for transmission.
There are 3 signals in the modulation process:
- The message signal (also called modulating signal): this is signal contains data that will be transmitted and has a low frequency. E.g. a voice signal
- Denoted $m(t)=A_m \cos(2\pi f_mt)$
- The carrier signal: a high frequency signal which will be modified in accordance to the message signal
- Denoted $c(t)=A_c\cos(2\pi f_c t)$
- The modulated signal: a signal that is the result of modifying the carrier signal in accordance to the message signal.
- Denoted $\phi(t)$
Consider this example: a voice signal is to be transmitted with amplitude modulation.
- The voice signal is the message/modulating signal
- The carrier signal is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency in the range of MHz.
- The modulated signal will have the same frequency as the carrier signal, but its amplitude will vary according to the message signal (hence “amplitude modulation”). For example,
- When there are loud voices in the voice signal, this will cause the modulating signal to have a larger amplitude.
- When there are quieter voices in the voice signal, the modulated signal will have a smaller amplitude.
- This changing size of amplitude in the modulated signal is how information about the voice signal is embedded.
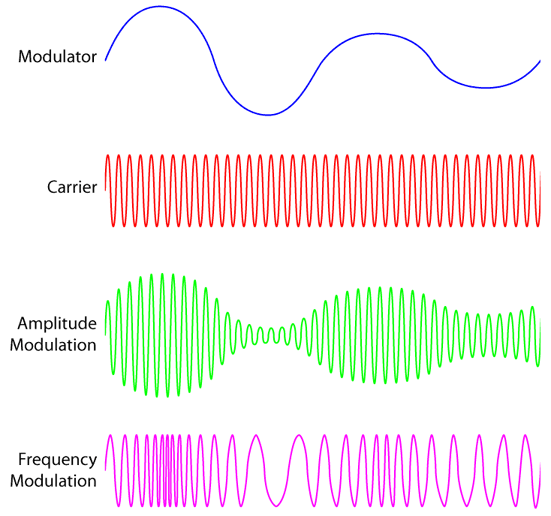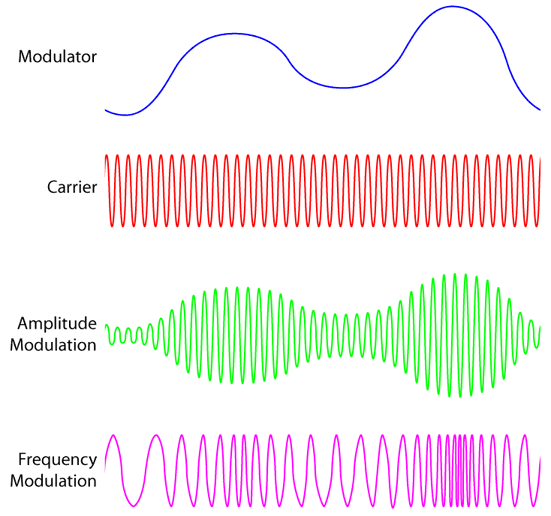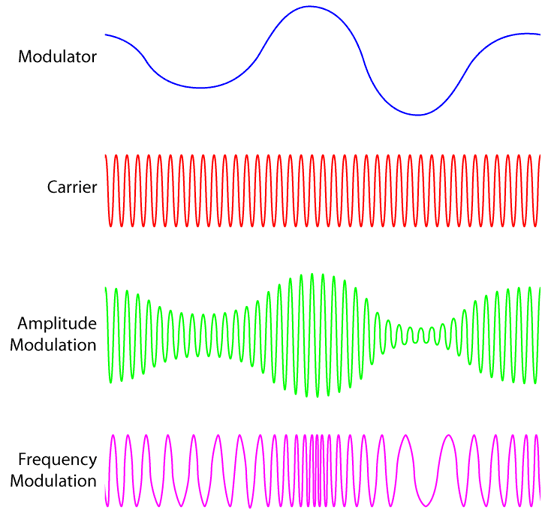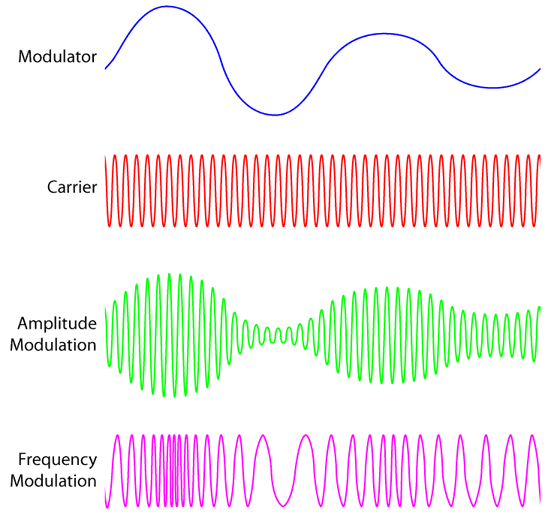
There are 4 categories of modulation, but in this section, we’ll focus on the two main types:
- Analog and digital modulation
